Are you thinking of going solar? There are three fundamental solar panel systems: on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems. The choice will significantly impact your solar energy costs and savings. So which best suits your home? We’ll table it all for you. Take a look at this grid-tied vs. off-grid system guide.
Grid-tied vs. Off-grid: Grid-tied Solar Systems
As its name suggests, a grid-tied system represents solar power directly connected to the utility power grid. Others may refer to it using terms such as utility-interactive, grid-back feeding, on-grid, or grid-tied system.
With this utility-interactive grid system, all you primarily need to do is to supply your solar electrical power to the utility grid. Then, in case your solar panels cannot adequately supply your needs, the electrical grid system will furnish you with additional power.

Illustrating the grid-tied system
Core System Components- Grid-Tied Solar System
The following are the main parts of a standard grid-tied solar system.
- Solar Panels
- Grid Tied inverters or microinverters
- Power meter
A solar system array showcasing the key components
Solar panels are the power source and, therefore, a fundamental component in all solar power systems.
Grid-tie inverter (GTI)
It is essential in the current and voltage regulation of the solar power system. Primarily, it changes the direct current (DC) from the solar panel to AC power. Most electrical appliances use power in AC form.
Some refer to this component as a grid-interactive or synchronous inverter. It is from its capability to synchronize the frequency and phase of the input current to meet that of the utility grid power lines.
Furthermore, the GTI raises the output voltage higher than the grid voltage. Consequently, this allows the flow of excess electricity into the grid.
Micro-inverters

Micro-inverters on individual panels
You can go for micro-inverters if you face roof shading issues, as they collect power from individual solar panels. Thus, unlike one central inverter, microinverters are many and thus more expensive than a single inverter.
However, their overall efficiency rates are higher than for string inverters.
Power meter
For this system, you need a special meter capable of net metering. This two-way meter will measure the power that goes in either direction of the grid system (from and to the grid).
Grid-tied Systems Advantages
1. It helps in savings
It offers the net metering option that allows you to save more money. Often, a solar system will produce more power than you actually need. Hence, the net metering option allows you to connect this power to the grid for electricity.
Many power companies purchase power at the same rate they sell to consumers. Thus, you’ll save a lot on power costs.
2. Has lower upfront costs
Under this system, you don’t need extra components such as solar batteries and battery-based inverters, which are pricey. Hence, regarding upfront costs, the grid-tie system is the cheapest.
3. It helps you save on maintenance costs
This system doesn’t have components such as battery banks. Thus, unlike systems with battery storage, it doesn’t require maintenance.
Grid-tied systems Disadvantages
- It can be pricey where power transmission lines are involved. Notably, its cost-effectiveness relies on the proximity to the power grid system.
- Secondly, in times of grid outage, you can not access power regardless of the prevailing solar output. It is because no bank battery can store power, unlike in off-grid systems.
Grid-tied vs. Off-grid: Off-grid Solar Systems
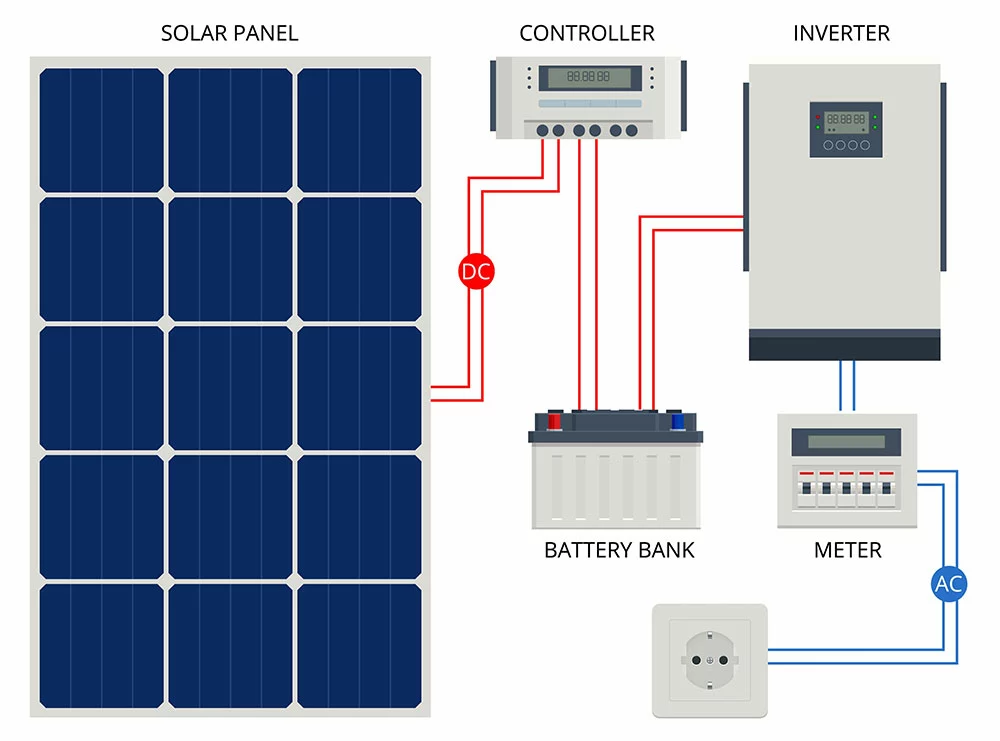
The off-the-grid solar system is the alternative option for those without access to the utility grid. But the off-grid solar battery system requires a unique set of components from the grid-tie system.

An off-grid solar power system illustration
Core System Components- Off-Grid solar power systems
For this option, you need the following additional components:
- Solar charge controller
- Battery bank (A bank is a series of batteries.)
- Off-grid inverter
- DC disconnect (additional)
- Backup generator (optional)
Solar charge controller/ Charge Regulator
The battery regulator will control the current rate in the battery bank, thus protecting it from overcharging. It keeps the batteries healthy, thus extending their lifetime. Also, note that most battery-based inverters feature integrated charge controllers.

A voltage regulator
DC disconnect switch
All solar power systems will need AC and DC safety disconnects, although off-grid solar installations require an extra one. You should install it between the off-grid inverter and the battery bank.
Its role is to connect and disconnect the current between these two components.
Battery bank
A battery bank or generator is a prerequisite for off-grid systems. It stores the power that the solar collects during the day.

A Battery bank
Off-grid inverter
You don’t need this component if your solar panel connects to DC-powered appliances. However, for AC-powered appliances, it will come in handy. Also, since typical off-grid solar systems don’t supply to the grid, their inverters don’t need to be in phase with the utility sine wave.
Backup generator
You may need backup generators to protect you from power outages, especially during the winter when the sun hours are limited.

A backup generator
Off-grid Solar Systems Advantages
- First, you can install the off-grid system in areas without access to power lines or the utility grid. The overhead transmission lines are pricey, and the off-grid system saves you from such costs.
- Also, it allows you to become self-sufficient and supply your energy needs. Thus, even during power failures in the utility grid, you remain unaffected as long as your solar batteries have power.
Off-grid Solar Systems Disadvantages
- Setting up an off-grid solar system is pricey in terms of upfront costs. You need to buy many components, such as battery banks which will cost you immensely.
- Your off-grid solar power system size will also be larger than an average grid-tie system. Hence, you need an extensive solar array to supply your energy needs in total, and this is pricey.
- Also, there are times you won’t have access to power. For instance, your battery backup may run out of power sometimes, and the sun may be limited, especially during cold months.
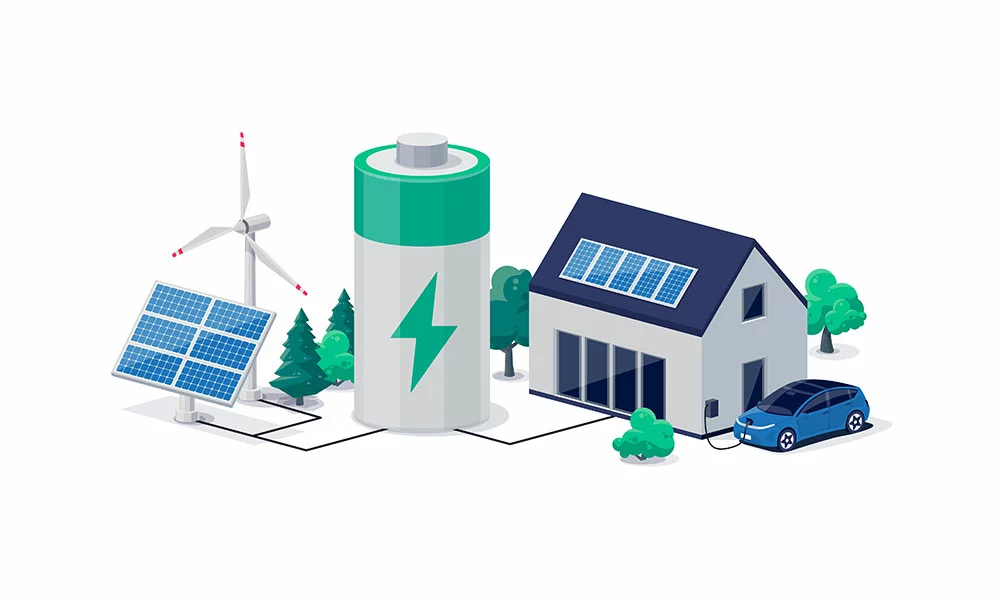
Grid-tied vs. Off-grid: Hybrid Solar Systems
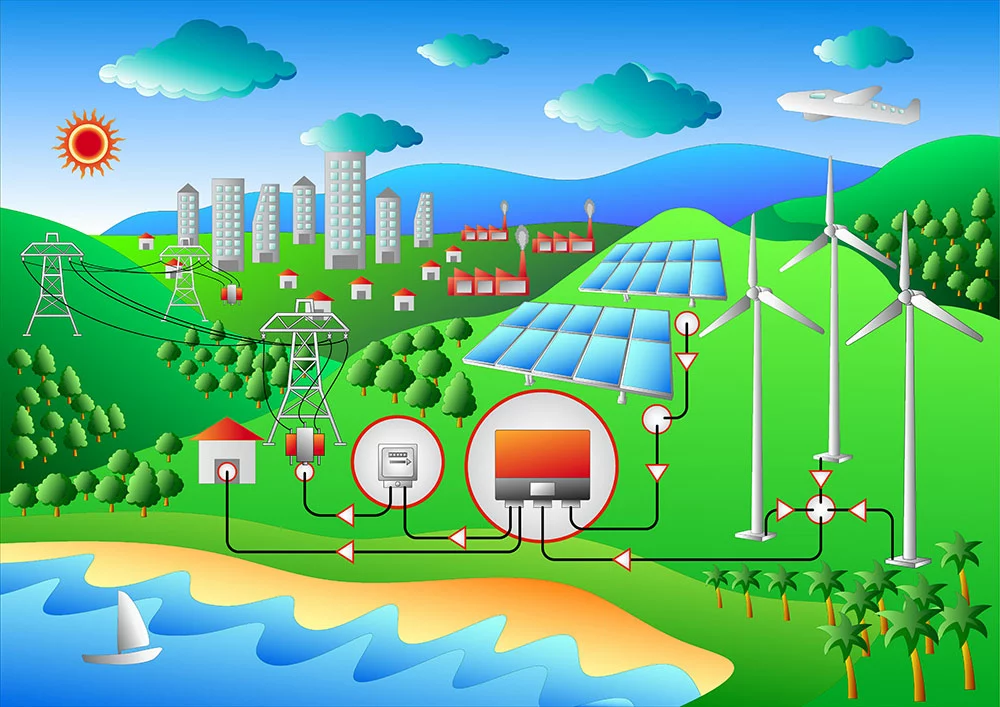

Wind and Solar Hybrid power system
Hybrid systems feature both properties of grid-tie and off-grid solar systems. For instance, you can have off-grid solar with utility backup power. Also, a hybrid system can comprise a grid-tied solar system with extra battery storage.
Notably, you have a typical hybrid setup if you have an electricity-powered car and a grid-tied solar system.
Core System Components- Hybrid solar power systems
The parts of a hybrid system are similar to those of a typical off-grid system we outlined earlier. They include the following:
- Battery bank
- Charge controller
- Power meter
- Battery-based grid-tie inverter
- DC disconnect (additional)
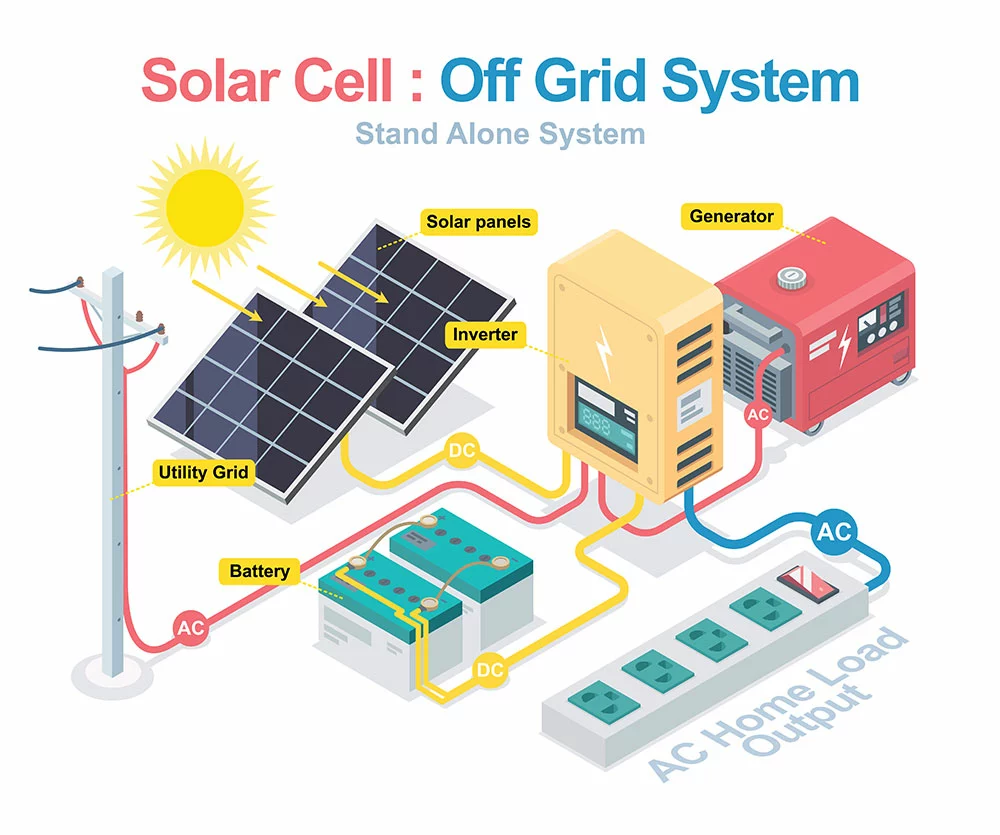
A solar hybrid system
Battery-based grid-tie inverter
Also called the hybrid inverter, the Battery-based grid-tie inverter works in two primary ways. Normally, they can synchronize with the utility grid and draw power from and to the battery banks.
Hybrid solar systems Advantages
- Compared to off-grid systems, hybrid solar systems are cheaper. Primarily, you don’t have to spend on components such as a backup generator or a series of batteries.
- Also, the hybrid system allows you to maximize your power and, in turn, lower costs. For instance, solar panels have the highest output during noon. Nonetheless, this time grid power costs peak. Hence, you can directly consume power from the solar system during such a time and save.
Hybrid solar systems Disadvantage
- The system is more expensive to set up than a typical grid-tie system.
Grid-tied vs. Off-grid: When in Doubt, Go Grid-Tied
Approximately 30 to 40% of off-grid system upfront costs are on battery purchases. They are also relatively expensive and could go up to four figures in dollars. Hence, if you’re unsure which of the two is best, go for the grid-tied option.
Grid-tie solar systems are cheap compared to off-grid systems, as storing power in the utility grid costs nothing.
Summary
Grid-tie, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems are the three main types of solar arrays. Each has its respective share of upsides and downsides, as outlined. We hope you’re now fully informed as you set up your solar array of choice. Thanks for reading, and feel free to engage us in case of any queries.
