Let’s get right into it! People have traditionally associated a bulb’s wattage with its brightness. However, since there are different bulb types, wattage is not the best measure of comparison for the brightness output. Therefore, you need to find the equivalent lumen output to replace CFL, incandescent, or halogen bulbs with LED light bulbs. In this article, we will explain the LED watt equivalent and give a wattage conversion chart to assist you in picking the proper LED bulb.
LED Wattage Equivalent Explained
If you have always associated a 60-watt incandescent bulb with a certain brightness level, then you might assume that every 60-watt bulb emits that brightness in lumens.
However, a 60-watt incandescent light bulb emits about 800 lumens, implying it consumes 60 watts to produce 800 lumens.

Incandescent vs. LED bulb.
But LEDs create energy-efficient lighting, consuming about 1/10 of the energy required by incandescent bulbs. Therefore, if you want to upgrade the 60-watt incandescent light fixture to LED, you should buy a 6-watt LED light bulb.
Such energy savings also translate to 1/10 of your energy costs, so expect cheaper utility bills.
Brightness: LED vs. CFL
LED and CFL bulbs don’t have a brightness difference intrinsically. The lumen output determines the brightness level because it is a measurement of light. Therefore, the two bulbs can have the same brightness in lumens but vary in their watts of power.

An LED vs. CFL bulb
CFL bulbs had an advantage over LEDs in the past because the latter did not produce omnidirectional light. However, the directional light from LEDs was better for recessed lights. But that was in the past. LEDs have evolved, and the current generation is better in almost all aspects. Be it energy consumption, durability, color temperature, or competitive pricing.
Why Wattage Is No Longer an Important Measure
The general rule of thumb with incandescent lights is that the higher the wattage, the brighter the light output. Generally, this rule applies to other bulbs when dealing with the same type.
For instance, a 10-watt LED bulb is brighter than a 6-watt LED. Similarly, a 100-watt incandescent bulb emits more light than its 60-watt counterpart.

A 10-watt LED bulb
However, wattage becomes irrelevant when comparing different bulb types.
Incandescent and halogen bulbs have highly inefficient wattage to light output conversions. Why? 90% of an incandescent lamp’s power input (wattage) gets wasted as heat. Therefore, you only get 10% of the energy consumed as light.
This energy efficiency explains why LED lighting with a 90% lower power rating will be as bright as the high-wattage incandescent lamp.
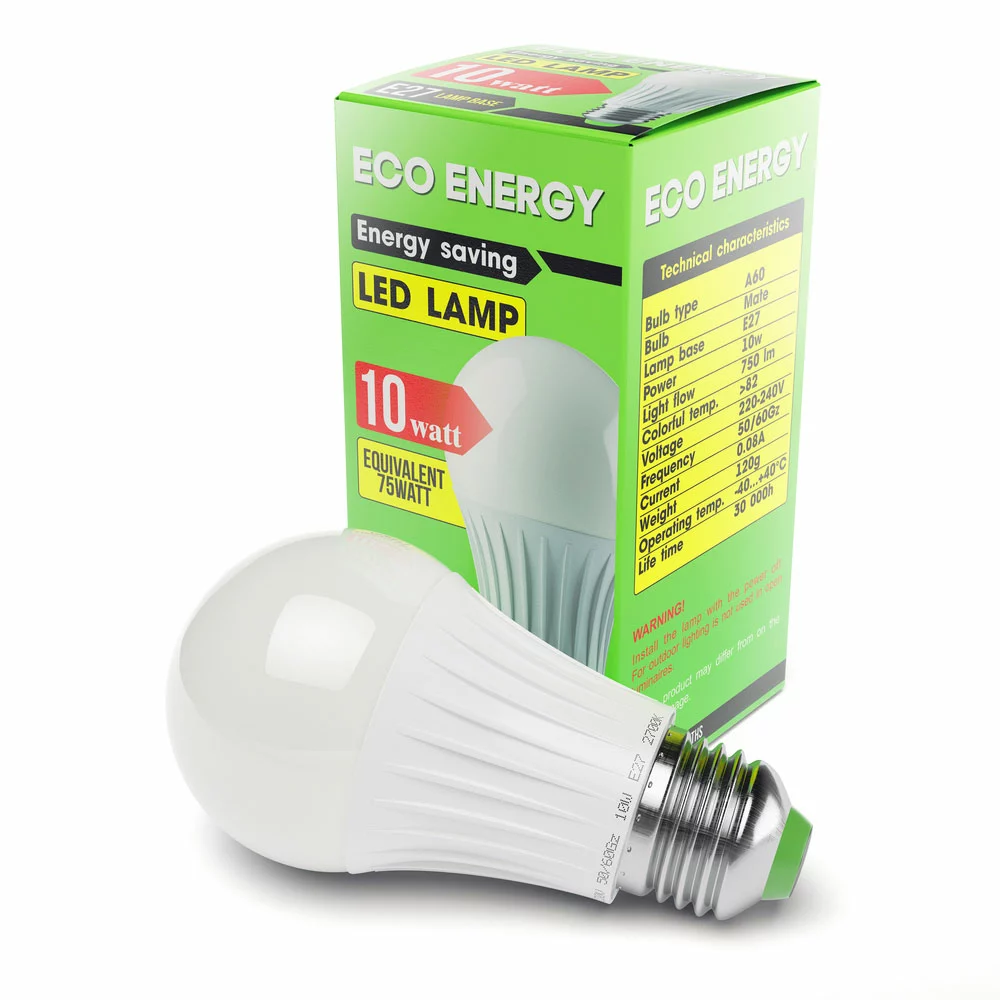
Although most LED bulbs give their wattage and lumen output rating on the packaging, most people pay attention to lumens, not the wattage.

An LED bulb’s packaging. Note the wattage and lumen rating, plus the equivalent incandescent bulb.
Therefore, the conventional wattage measurement will end as homes and businesses phase out incandescent and other inefficient bulbs and adopt LEDs.
Wattage Conversion Chart
Since wattage does not reflect the truth anymore, it is necessary to have a wattage conversion chart when switching to new generation LEDs.
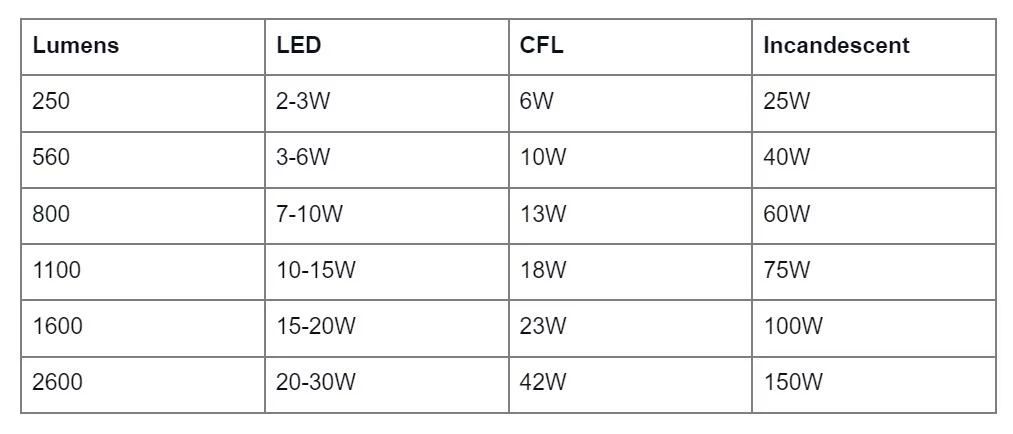
Incandescent bulbs produce approximately 15 lumens per watt, while their halogen counterparts emit 25 lumens per watt. CFLs take the output up to 60, and LEDs produce roughly 72 lumens per watt, making them the most energy efficient.

A compact fluorescent bulb
When upgrading your lighting, you don’t have to worry about going above a fixture’s wattage requirement because LEDs consume significantly less.
Cost Effectiveness: LED vs. CFL vs. Incandescent
LEDs are undoubtedly more energy efficient than the other bulb types. However, even though their prices are becoming more competitive, they are still more expensive to purchase. Therefore, it would be wise to compare the lifetime energy savings and total cost to determine which bulb gives you the best deal.
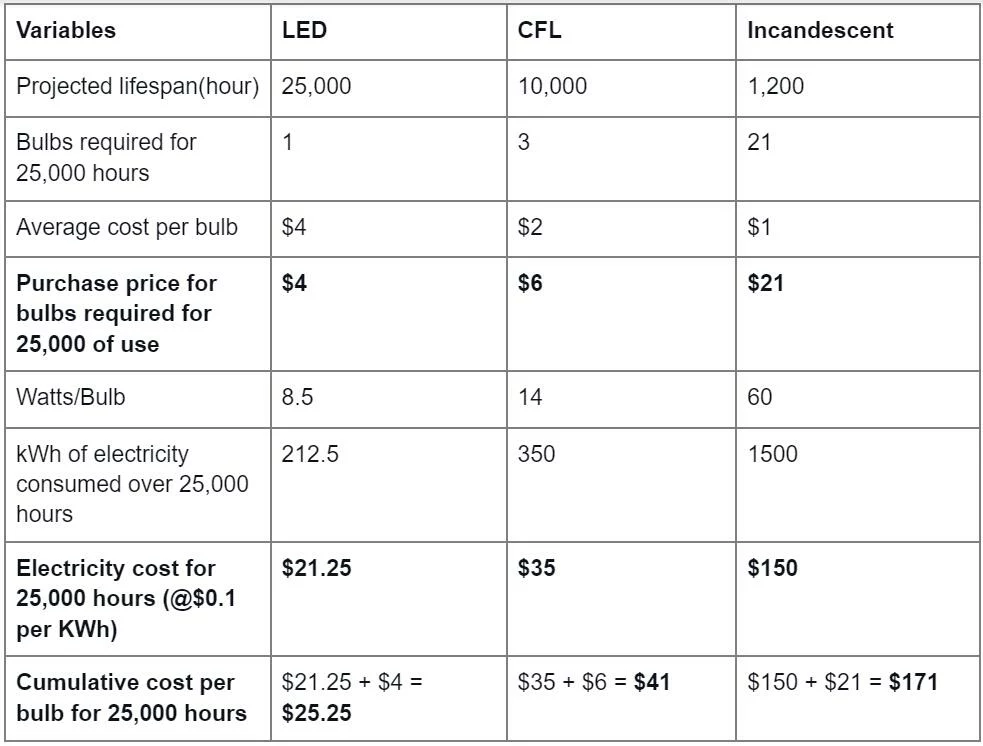
The price difference range widens if you consider the practical application. For instance, the average household might have 25 bulbs. The cost for these bulbs would amount to the following.
| LED | CFL | Incandescent |
| $25.25 x 25 = $631.25 | $41 x 25 = $1025 | $171 x 25 = $4275 |
Therefore, switching from incandescent to CFL will save you $3,250. On the other hand, switching from incandescent to LED will save you $3,643.75.

A 12-watt LED lamp with a 40,000-hour lifespan
However, the bulb and electricity costs can vary. The bulb’s lifespan can also vary, so the figures above can change. But generally, the overall prices of LED bulbs are lower than the other types in the long run.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, the LED wattage equivalent when comparing bulbs is not difficult to grasp. Since wattage is proving irrelevant, you should consider the lumen output as the basis for this comparison to determine the right LED bulb to buy, and the table above will help you in this process. That’s it for this article. If you have any questions or comments, contact us for more details.
