Today, solar power is arguably one of the fastest-growing clean energy sources. However, at one historical point, it was not a key electrical energy source despite solar energy being available freely. So when was the tipping point where we discovered that we could convert solar energy into electricity? We have covered the journey to modern-day solar power systems and invite you to have a glimpse of critical points in the solar energy timeline.
When Was Solar Energy First Used?

A Roman Bathhouse Illuminated by the Sun
Solar power has been in existence for as far as we know. An inquest into the 7th century B.C history reveals that solar energy was useful primarily in lighting fires. Also, solar power was conventionally essential in lighting religious ceremony torches in Greek and Roman civilization.
In addition, at around 20A.D., the Chinese civilization used solar energy via mirrors for illumination. Medieval Roman bathhouses also featured massive windows facing the sun’s direction to harness it for warming the rooms.
But none of these early applications were as sophisticated as today’s solar cell technologies. So how did modern-day solar energy systems, specifically solar panels, come? Check out below.
Solar Energy Timeline
Do you know the 1973 oil embargo? If you are not aware, this was when the US was short of gas supply. Also, it marked the first time the country became fully conscious of the significance of solar technologies and began solar incentives.
But what are some key events leading to solar adoption as a key renewable energy source? Check out this timeline.
Discovery of the first solar cell- 1839
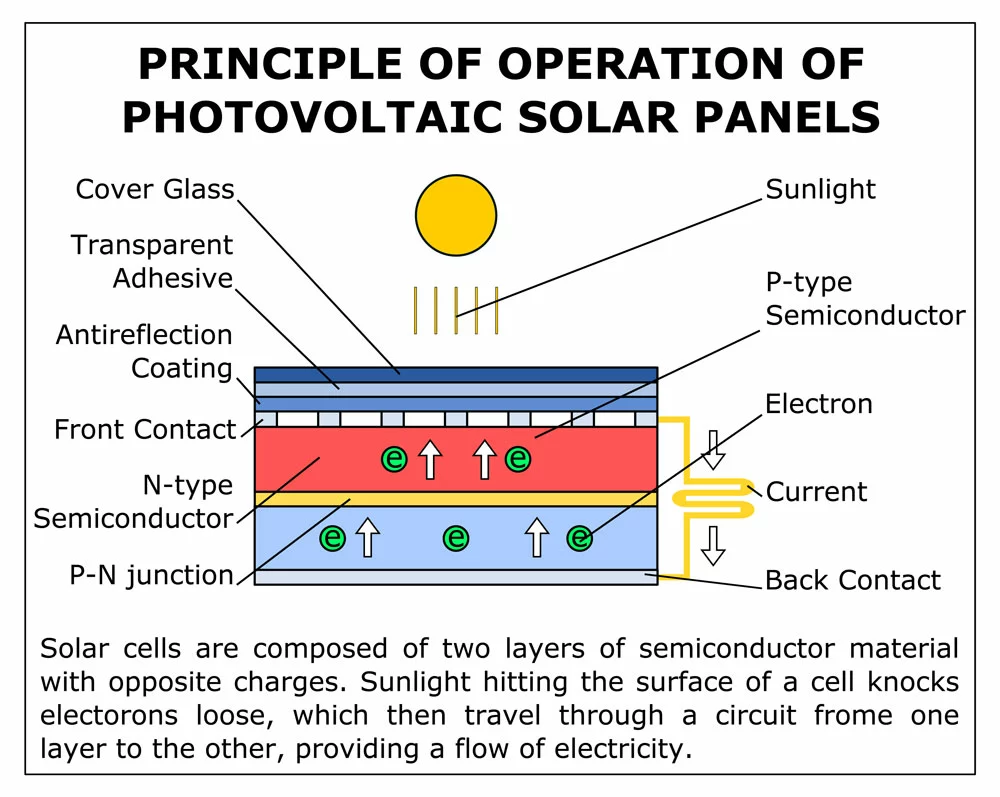
Photovoltaic cells principle
We owe credit to Alexandre Edmond Becquerel for discovering the initial photovoltaic cell/ solar cell. The French physicist- then 19 years old, was conducting experiments using an acidic solution and metal electrodes. He then discovered the photovoltaic effect that is the basis of contemporary solar cells.
Operationalization of the first Solar Panel- 1883
It was until 1883 when American inventor Charles Fritts came up with selenium wafers solar cells. Earlier, Willoughby Smith had identified the photovoltaic properties of selenium.
The 1st United States Solar Cells patent- 1888
This year, Edward Weston gained the first solar cell patent. It set the basis for further research on solar electricity and energy-efficient solar panels.
The 1st United States Solar panels Patent- 1901
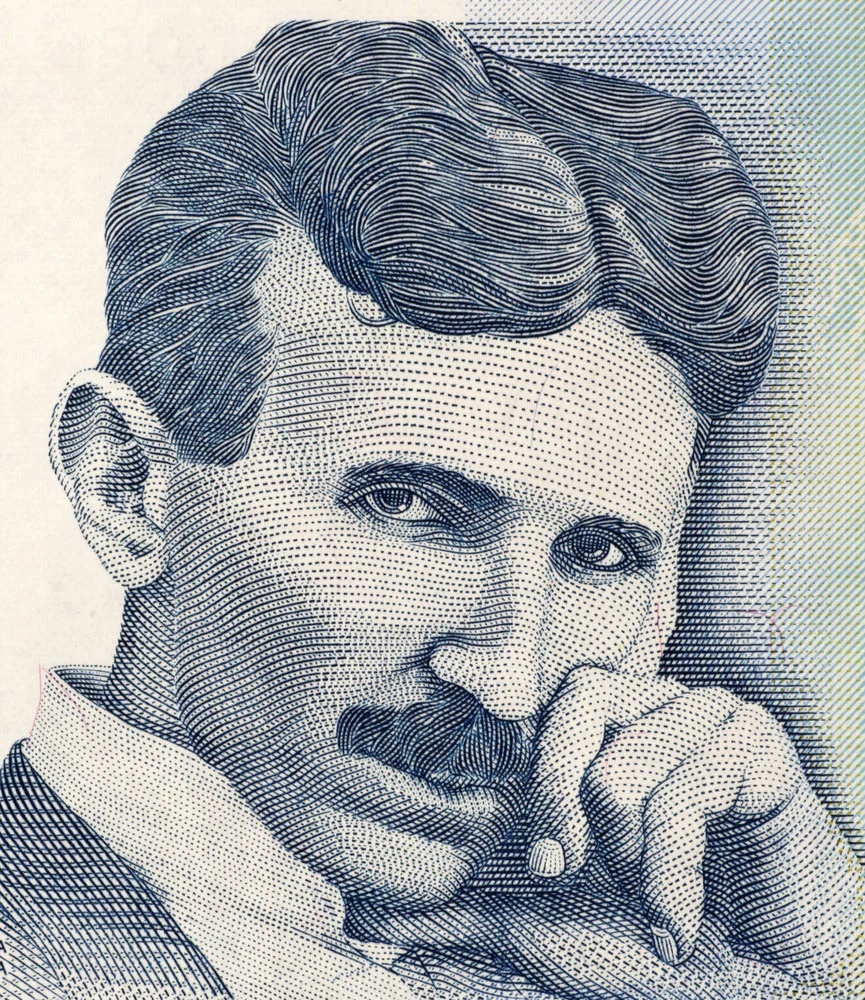

Nikola Tesla received the first solar panel patent.
Nikola Tesla is widely renowned for the discovery of AC current. But, he was also the first scientist to receive a solar panel manufacturing patent. At the time of issuance, the issuing body called it an apparatus to utilize radiant energy patents.
Albert Einstein confirms the photoelectric effect-1905
Renowned physicist Albert Einstein introduced the photoelectric effect phenomenon in 1905. It marked immense progress in solar technologies by confirming how solar cells could convert sun rays to electric current. Albert Einstein would later win a Nobel Prize in 1922 for his discovery of the photoelectric principle.
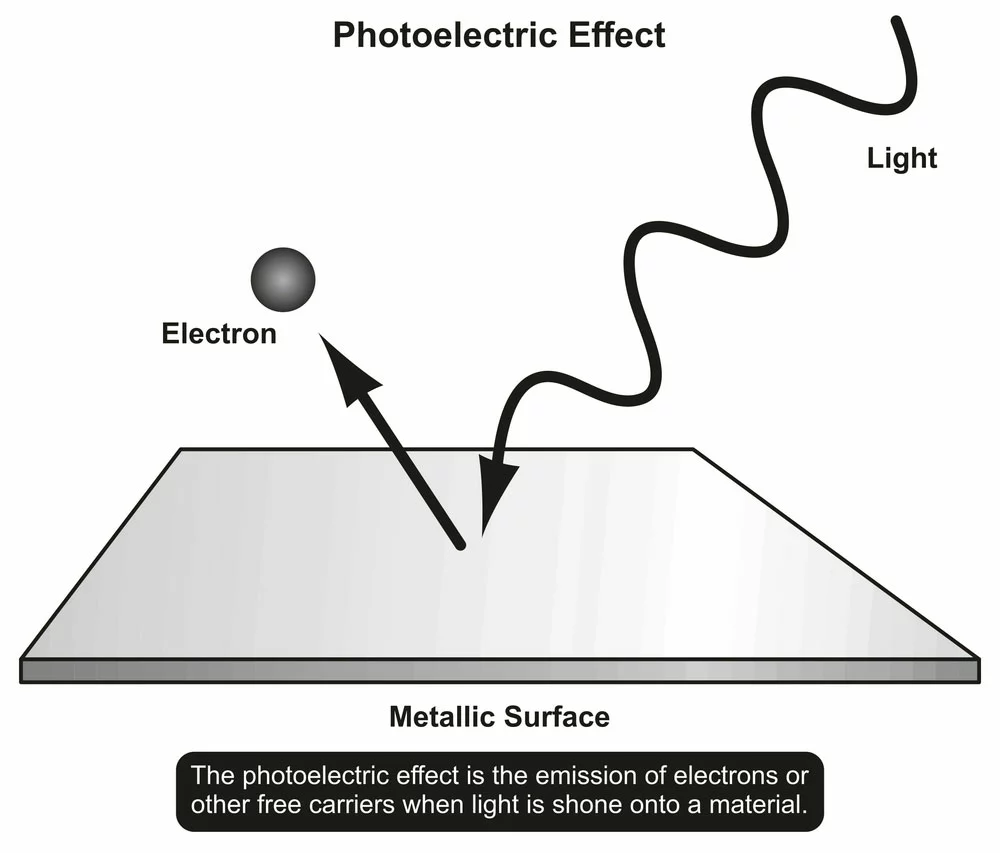
Photoelectric effect
Confirmation of the photoelectric effect- 1915
Ten years after its introduction, Robert Millikan ascertained the photoelectric effect principle via experiment. This confirmation was immense in the power sector and set the precedence for Albert Einstein to win the 1922 Nobel Prize.
Manufacturing of the 1st high-power silicon solar PV cell- 1954
Bell Labs physicists- Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson created the first silicon solar PV cell in 1954. This cell used silicone instead of the formerly used selenium wafers. Hence, it improved energy conversion rate and efficiency.
However, although Exxon Mobile owned Bell Labs, the mother company went back to using fossil fuels even after this discovery.
Mass production of solar panels- 1963

Numerous photovoltaic cells
In 1963, Sharp Corporation produced massive photovoltaic cells, setting the ground for other companies to take up the manufacturing. Also, Japan set up a 242-watt PV array, arguably the largest solar installation.
Solar Panel in the Outer Space- 1964
NASA launched a 470-watt PV array Nimbus Satellite into space in 1964. It was preceded by the Naval Research Laboratory’s launch of the Vanguard I in 1958. Vanguard I featured a solitary one-watt panel for powering its radios.
Hence, the 1964 launch of a larger watt array significantly improved the former solar panel. Later, in 1966, NASA went a notch higher, launching the world’s first Orbiting Astronomical Observatory. It drew power from a one-kilowatt array of solar panels in another positive step in solar energy technology development.

The International Space Station
First fully solar-powered building – 1973
Massive research into clean energy technologies in the 1970s, such as solar. Consequently, there was a significant reduction in silicon photovoltaic cell costs by approximately 80%.
Also, in 1973 the University of Delaware set up the first solar-powered building. The building entirely relied on solar thermal energy from PV panels.
Still, in the 1970s, Kyocera Corp manufactured the world’s first thin-film silicon ribbon crystal solar modules. This move was key to the simplification of modern-day solar panel manufacturing.
Formation of National Renewable Energy Laboratories- 1977
In 1977, the U.S. Department of Energy formed the U.S. Solar Energy Research Institute. They later renamed it National Renewable Energy Laboratories (NREL). The primary mandate of this body was renewable energy research.
100,000 Solar Roofs program- 1999

A solar cell farm power plant
The German government dedicated $500M to the “100,000 Solar Roofs” program in 1999. The project aimed to subsidize the residential solar industry when solar panels were costly. Thanks to the project, there was a significant take-up of solar technologies and further research into cheaper solar solutions.
However, in 1994, Japan piloted a similar project called the “70,000 Solar Roofs.”
Solar Energy Timeline: Investment tax credit on Solar Panels- 2005
In 2005, US President George W. Bush signed the Energy Policy Act of 2005 into law. It sought to provide a 30% investment tax credit (ITC) for those who invested in solar energy systems.
The tax incentives programs were vital in allowing access to affordable solar panels to people in a drive to encourage clean energy adoption.
It was followed by several other State Level subsidy programs, such as the California Solar Initiative (CSI), launched in 2006.
Solar Energy Timeline: Further Investments in Clean Energy- 2007

Clean and Unclean energy sources
As of 2007, the global clean energy investment stood at over $100 billion. Notably, solar energy became the most widely adopted clean energy source. The solar tax credits were central to this growth, especially in the US.
Further, the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 extended the solar ITC subsidy program by eight more years. In addition, between 2008 and 2012, Germany, Australia, Spain, and Italy introduced new solar subsidy programs.
In turn, the PV module costs significantly plummeted, giving more an opportunity to acquire solar panels.
Solar Energy Timeline: Large-scale solar production factories- 2010 to 2018

A Solar cell power plant
The entry of Chinese solar panel manufacturers was vital as it significantly lowered the cost of solar to $.70 per watt. Also, in 2015, there was a record high residential solar power installation in the US, marking the industry’s significant growth.
Furthermore, in 2015, car manufacturer Tesla launched Powerwall- lithium-ion battery storage. And this was key in ensuring the efficiency of solar power harnessed during the day for use at night.
Solar Energy Timeline: Federal income tax credit extension- 2015
The U.S. Congress further boosted the uptake of photovoltaic solar power systems by extending the 30% tax credit by eight more years. Thus, the subsidy was to end in 2021. Nonetheless, it is still present in 2022, meaning that solar installation costs are remarkably lower than in the past.
Solar Power Today

Wind and Solar power plants
Solar panels are now easy to create and install; thus, many homes have adopted them significantly. Also, there are increasing campaigns in the US and other world parts for people to adopt solar systems as an alternative to fossil fuels.
There are currently more solar panels in California than in any other US state. But, there is increasing adoption in many other states, such as Rhode Island and Texas. Globally, Asia leads in the number of solar panel installations and is closely followed by Europe.
Future projections show that solar energy adoption will continually increase as the world tries to break from the overreliance on fossil fuels.
Summary
Solar energy has been ever available and abundant since the beginning of time. And while it has taken us a long time to get to the current solar energy utilization, the recent progress is encouraging. Solar electrical power adoption remains the leading solution to the current fossil fuels energy crisis we’re experiencing. That’s all for now. Thanks for taking the time to walk with us through solar energy in history.
