Do you know what anti-islanding is and why it’s so important? If not, you’re not alone! Anti-islanding can be a confusing concept since it impacts using electrical supply.
Anti-Islanding is a safety measure that shuts off solar power in an emergency or power outage. As a result, this protects users or utility workers from any damage.
In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of anti-islanding. Let’s get started!
What Is Solar Islanding?
Solar islanding occurs when a solar array continues to work even after the grid goes down. Many users think it is good that solar power systems continue to work even when the grid goes down. Yet, this can be dangerous, as it increases the risk of shock or other injuries due to excess power.

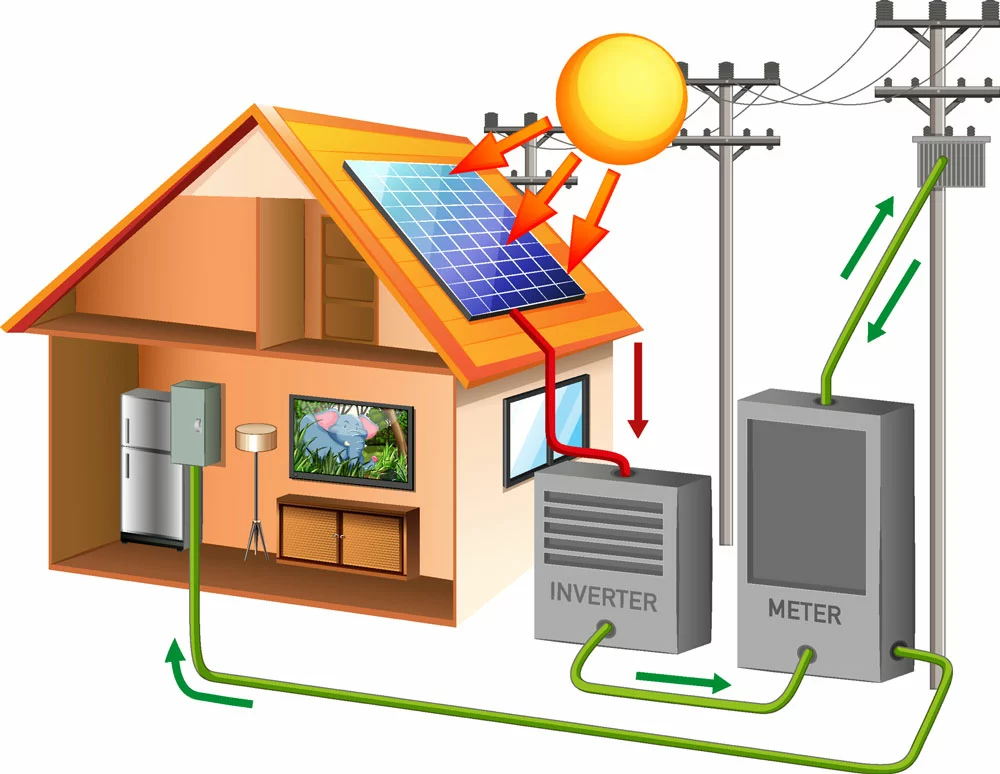
Solar power systems
Grid-Tied Solar Vs. Off-the-Grid Systems
Maybe you’re thinking about using solar grid systems. So, it would be best if you understood the difference between grid-tied and off-the-grid systems.
A grid-tied system can work in conjunction with the electrical grid. But an off-the-grid system is completely independent. So, anti-islanding measures work for grid-tied systems but not for off-the-grid systems.

An off-grid solar power system illustration
What Is Solar Anti-Islanding?
Solar anti-islanding is a safety feature built into the grid that helps to protect both solar panel users and power grid operators. It works by disconnecting solar panels from the grid during a power outage so that these panels are not feeding electricity back into the system when it is down. It helps to keep line workers and anyone else in the area safe, as there is no risk of being electrocuted due to electricity circulating within the affected grid.

Solar array
Why do we need Anti-Islanding Protection?
The main reason for anti-islanding protection is safety. Without it, your solar panels could continue to produce electricity during a power outage, potentially causing harm to utility workers trying to fix the grid.
Anti-islanding protection also helps prevent damage to your home’s solar panels and electrical equipment during an outage.
Additionally, anti-islanding measures help maintain the integrity of the power grid. When solar panels continue to work during a power outage, they can cause voltage fluctuations and potentially damage grid equipment.
So, not only is anti-islanding important for safety reasons, but it also helps ensure the smooth operation of the power grid as a whole.
How Does Anti-Islanding Work?
When the grid goes down, your inverter will detect the loss of power and disconnect from the grid within milliseconds. It prevents your solar panels from feeding electricity into a downed power line, which could be dangerous for utility workers.

Illustrating the grid-tied system
Islanding Detection Methods
The anti-islanding techniques each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Your choice will depend on the specific needs of your home or business. Whatever method you choose, ensure that you have reliable anti-islanding protection.
Passive Methods
These methods depend on the normal operation of the grid to detect power island issues. Some common passive anti-islanding methods include:
- Under/Over Voltage
This anti-islanding technique monitors the voltage on both sides of the grid. The voltage on one side is higher or lower than the voltage on the other side. Then the anti-islanding measures will change the voltage state.
- Under/Over Frequency
This protection works on frequency measures on both sides of the grid. Then, it triggers the measures if there is a significant difference.
One more advantage of this technique is that the protection can work at lower voltage levels. This method can help prevent damage or accidents due to an under-voltage condition.
- Rate of Change of Frequency
It detects the rate of change of frequency (ROCOF). Next, it will trigger anti-islanding measures if there’s chaos in frequency. Also, this transient signal is useful because it can be set to detect a wider range of voltage fluctuations.
- Voltage Phase Jump Detection
Loads connected to a distribution grid can cause voltage phase jumps. These anti-islanding techniques track the ripple current on the power line. The system will take action if voltages are out of sync.
- Harmonics Detection
Total harmonic distortion is a harmonic measurement present in an AC electrical system. So, these techniques check the AC system for large fluctuations in THD. Then, it will take the necessary steps to protect the system.
The Grid-tied system with Solar Inverter
Active Anti-Islanding Methods
- Negative-Sequence Current Injection
This technique injects negative currents onto the grid. Then it monitors the current responses to detect the fault condition.
- Impedance Measurement
This method identifies the anti-islanding state by measuring impedance changes in the grid. They use an impedance analyzer and an anti-islanding protection device. Then they detect the differences between impedances on each side of the grid.
- Impedance Measurement at a Specific Frequency
Impedance measurement at a specific frequency is like other anti-islanding detection methods. Yet, it measures impedance over a wide range of conditions and frequencies rather than one. Also, it identifies the condition even if there are large fluctuations in the grid supply.
- Slip Mode Frequency Shift Detection
We use this when a generator or other power device reverts to “slip mode” or becomes unstable.
This technique relies on advanced sensor technologies, such as optical sensors. It will identify slip mode frequency shifts and trigger anti-islanding measures.

A backup generator
- Frequency bias
Frequency bias is both reliable and easy to set up. This method monitors the system frequency and compares it to a stored reference value.
We use this method when there are significant deviations from the reference value. Then, the device will trigger anti-island conditions.
Utility-based Methods
- Manual Disconnection
This anti-islanding method relies on workers from utility companies to disconnect the grid with a transfer switch. While this may be a simple option, it needs extensive training. Also, it can result in longer periods of downtime for consumers.
- Automated Disconnection
Unlike manual disconnection, automated disconnection does not need any manual intervention. This method relies on advanced algorithms to detect the state and trigger protection. Also, this method is more reliable than manual disconnection. But it can be quite costly to install in the power industry.
- Transfer-Trip Method
Utilities can discover faults, whether through automation or by examining the recloser. So they can use this information to send it down the line.
The grid has working automated recloser systems and external communications systems. You can use this method to force the tripping of DG systems by opening a series. And this will isolate the DG system and remove it from the NDZ.
- SCADA
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition is a communication network. It can track, manage and control grid assets. When grid conditions become unstable, the protection devices communicate with SCADA systems. Then it will trigger the anti-islanding measures.
Islands of the Future
Anti-islanding protection devices and systems are essential for ensuring a reliable power grid. But many experts predict even more advanced anti-islanding technologies in the future.
For example, they are working on solutions that rely on AI and machine learning. It will detect changes in grid conditions and measures without any hazards.

Renewable energy smart power grid system.
Summary
That was a lot of information on anti-islanding protection. Anti-islanding is all about preventing power outages and maintaining reliable grid operations.
Whether you are looking for anti-islanding protection for industrial or residential applications, many different methods are available to suit your needs. Thanks for your time.
