As wind turbine technology advances, the world expects the industry to grow and expand its capacity globally. However, this is not without its flaws — wind energy pros and cons. Proponents say it provides safe, reliable, and inexpensive power with minimal environmental impact.
On the other hand, detractors argue that the technology isn’t as environmentally friendly as once thought. The truth probably lies somewhere in between these two extremes. This article will comprehensively overview the pros and cons of wind energy and everything else you want to know.
What Is Wind Energy?

Wind turbines
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the wind to produce electricity. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of moving air into electrical power. In 2021, Wind energy produced 9.8% of all U.S electricity and is still growing steadily.
How does wind power work?
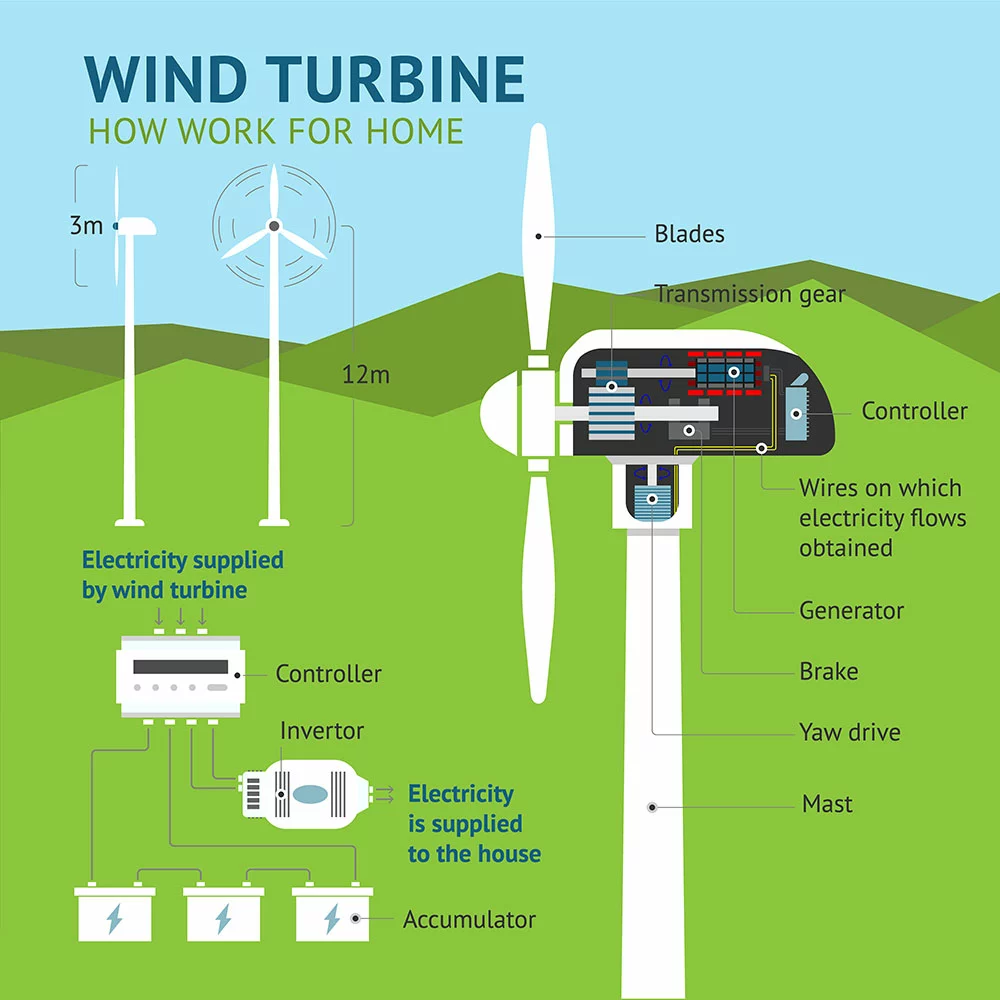
How wind turbines work
Wind power works by using the wind to turn blades that are connected to a generator. The process starts by tapping the wind into a turbine, which rotates to create kinetic energy. Then, this kinetic energy is converted into mechanical energy, which spins a shaft connected to an electric generator. As electricity flows from the generator through wires to homes and businesses, it reaches its final destination as usable power for consumers.
Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind power has many advantages over other forms of renewable energy. These can be categorized into environmental and socioeconomic.
Environmental Advantages of Wind Energy
- Wind energy is clean. It does not produce greenhouse gases when used to generate electricity, so it’s an environmentally friendly power source.
- Wind farms can be built in many places, including remote areas like the ocean and deserts. They are also relatively inexpensive to build and maintain.
- It’s a reliable source of electricity since the wind blows most of the time in most places.
- Wind farms don’t require fuel for operation.
- Wind energy is renewable. This means we cannot deplete or reduce the quantity no matter how long we use it, which makes them a better choice than coal or natural gas power plants.
Socioeconomic Advantages of Wind Energy
- Wind farms generate tax revenue through sales taxes on equipment purchases and property taxes on land used for turbines.
- It also helps improve rural areas’ economies by providing local employment opportunities.
- This energy source is one of the cheapest forms of power available today. This is because the turbines do not require fuel to power them, and their maintenance cost is relatively low.
- Wind power also reduces the dependence on coal and gas for electricity generation.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
Like any other form of renewable energy, wind energy has its shortcomings. Here are some of the disadvantages of wind turbines:
- It is intermittent. Wind speed varies widely over time and space, so one cannot entirely rely on it for a steady power generation or backup power supply.
- Wind turbines are noisy, which can annoy people living near them.
- Wind turbines require maintenance and replacement parts, which are expensive. They also require significant amounts of land, which adds to their cost.
- Wind farms also hurt wildlife and bird populations due to their noise. When birds, bats, and other flying wildlife collide with moving turbines, they have a slim chance of survival.
- Many people don’t want to see turbines in their communities because they’re an eyesore. However, this varies across individuals and is more of a preference issue.
- You can only harness wind energy in locations where wind speed is high.
- Most turbines are built in remote areas with no power transmission lines to the cities and homes. This makes the initial setup cost to be high.
Uses of Wind Energy
Illustration of wind energy use.
The wind energy industry is growing daily and has many uses.
- Wind power can power vehicles. Instead of using fossil fuels, you can use wind turbines to power your car or truck. A good example is a wind-powered car that covered 3100 miles through Australia.
- Sailing Cargo ships can use wind power to propel their vessels through the water using sails or propellers rather than using engines that would require fuel and cause pollution.
- Wind farms generate an enormous amount of electricity for entire power communities. Now more people are harnessing wind energy to power their homes and businesses at cheaper costs. Wind energy accounts for 25% of the electricity produced in eight states in the U.S.
- You can use wind turbines to pump water from wells or reservoirs. While pumping underground water is not a new technology, wind energy is cheaper and energy efficient.
Balancing the Pros and Cons of Wind Energy
Wind energy is a huge part of the future of our planet. It’s clean, renewable, and a resource that is available in abundance. But wind energy also has its drawbacks — for instance, it’s not always reliable or consistent.
Wind turbines also produce noise pollution; they make noise while they’re working and when they are not spinning fast enough to generate electricity.
But there are ways around these issues. With technological advancements, newer turbines produce less noise, which is a positive step toward reducing noise pollution. Also, as the world forges a united front in fighting climate change, nations are heavily investing in more research and development to better the wind energy industry.
Political and industrial developments have steered a positive upsurge of environment-friendly wind turbines. Again, individuals have a role to play in reducing carbon footprints. This can be through planting trees to replace those affected by the construction of turbines.
FAQs
How much energy does a wind turbine produce?
A typical onshore wind turbine may generate between 2 and 3 megawatts (MW), or more than 6 million kilowatt hours (kwh), annually. This will be adequate to satisfy the electrical needs of roughly 1,500 average households.
Is wind energy expensive?
Wind energy is economical Land-based, utility-scale wind turbines are among the most affordable energy sources accessible today. Additionally, as wind energy research and technology evolve, its cost-competitiveness continues to rise.
Does wind energy cause pollution?
Compared to many other energy sources, using wind energy generally has less impact on the environment. The turbines produce little to no harmful emissions.
The future of wind energy
Wind turbines have come a long way since their inception, and they’re still improving. There have been evident improvements in turbine size, materials, and power output in the past few years.
That’s not to mention the innovations still happening and coming down the pipeline. These include better ways to capture more energy from wind turbines so people can use them more efficiently. Also, the cost of wind power has dropped considerably in the past few decades, and it is steadily improving as technology advances.
In the future, wind power will supply 35% or more of the world’s energy demands, overtaking all other generation sources. Additionally, it might accomplish the nearly quarter of yearly CO2 emission reductions required by 2050.
Summary
Wind energy is renewable, clean, cost-effective, and a powerful supplement to the current energy market. This technology has been in use for more than two centuries. Since then, there’s been plenty of advancements that have made it a truly viable renewable energy option for many consumers. With the number of Americans harnessing wind power increasing yearly, the business is only expected to grow. Whether you’re a homeowner who wants to get more from your property or an electric utility looking to decrease your reliance on fossil fuels, investing in wind energy can be a prudent decision.
