You’ve probably heard of passive solar savings, but you’re unsure how it works or if it’s worth the investment. Passive solar savings is an energy-efficient way to save money on your annual energy bill while also doing your part to be more environmentally friendly. In this article, we’ll discuss passive solar savings, how it works, and some of the benefits you can expect from using it in your home.
What Is Passive Solar Energy?
Passive solar energy is a method of harnessing the natural heat and light from the sunlight to provide heating, cooling, and lighting for buildings.
Passive solar systems differ from active ones because they don’t use mechanical or electrical devices to capture and distribute solar energy. Instead, they rely on the design of the building itself to maximize the absorption and distribution of solar energy.
Advantages of Passive Solar Energy
1. No Need for Direct Sunlight
A passive house aims to block out direct sunlight to maintain a cool temperature.
2. Cheaper
Passive solar energy does not require special equipment or installation, reducing costs further.
3. Less Noise Pollution
Using trees and insulating windows reduces noise pollution and keeps the temperature inside your home consistent.
4. Low Maintenance Costs
Once you have a passive solar system installed, there’s not much you need to do to maintain it. It makes a “set-it-and-forget-it” type of system, which can save time and money in the long run.
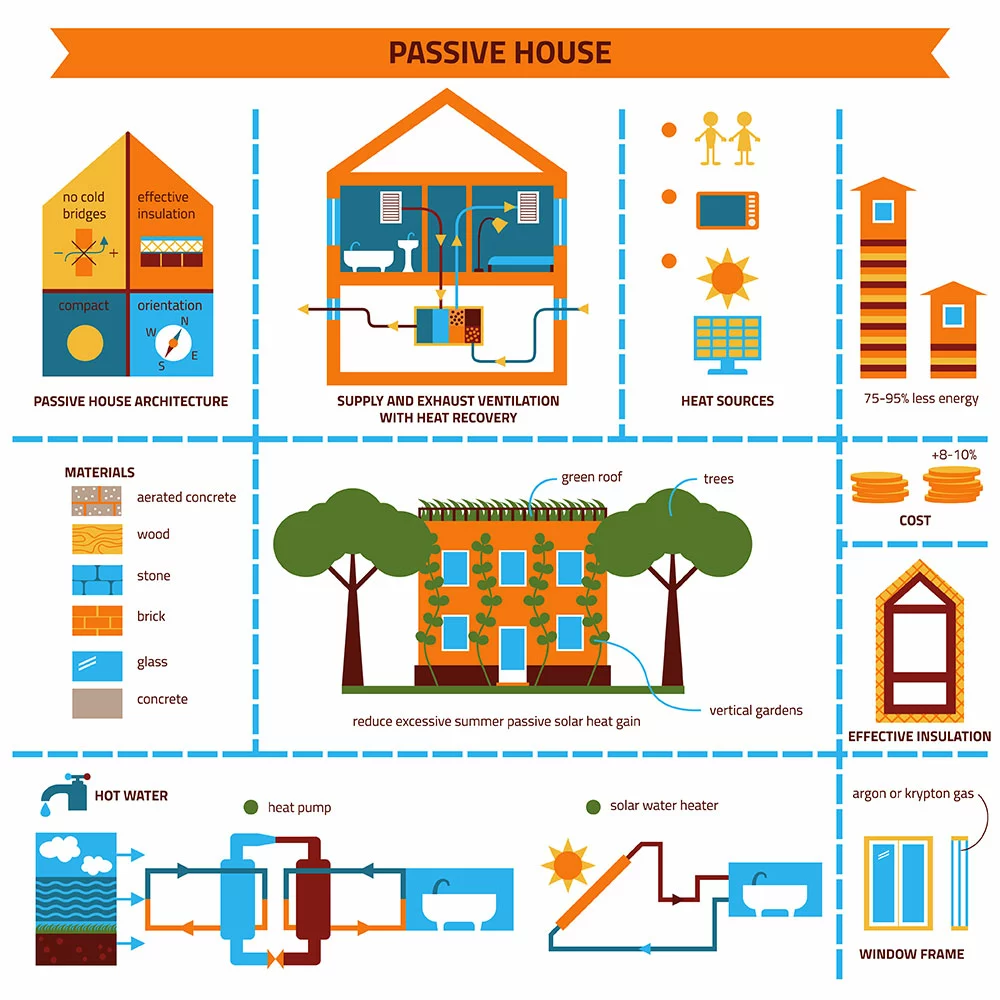
The passive solar house system
Disadvantages of Passive Solar
- Passive solar homes require professionals, but this is necessary for any upgrades to the home.
- Upgrading an older home to a passive solar design or using solar panels isn’t cheap because the home might not have proper insulation.
- Passive solar design is often limited by the features of a building that you can’t change.
Understanding Passive Solar Home Design
There are some basic elements necessary for a successful passive solar home design, including:
Windows Orientation
Properly oriented windows can help reduce the amount of artificial lighting and heating needed in the home. They should be placed within 30 degrees of true south and not shaded during the heating season. On the other hand, shading during the spring, fall, and hot seasons will help prevent overheating. Plus, It would be best to keep window glass clean for maximum heat absorption.

Windows of the building
Passive Solar Savings: Thermal mass
It is typically made from brick, stone, and tile. These materials can absorb heat from the sun during the summer and the house’s warm air during the cooling season.
Even though other materials like water and phase change products can store heat better, masonry is still popular due to its ability to serve multiple functions. You can use masonry as part of the actual structure of a building, as well as a finish material. It creates aesthetic appeal while still providing useful thermal mass properties.
To ensure the maximum benefit from thermal mass materials, position these materials in areas that receive direct sunlight throughout the day.

Masonry wall
Passive Solar Savings: Heat Transfer Mechanisms
There are three main ways of solar heat distribution:
- Conduction: When two objects interact directly, heat will flow from the hotter object to the cooler object. The heat transfer rate depends on the material’s conductivity and the temperature difference between the two objects.
- Convection: heat transfer through fluids, such as water or air. When heat is applied to a fluid, the molecules of the fluid expand and become less dense. The less-dense molecules then rise to the top of the fluid, while cooler, more dense molecules sink to the bottom.
- Radiation: the transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves. When you stand in front of a fire, radiation transfers heat from the fire to your body. This process occurs because your skin absorbs infrared waves emitted by the fire.
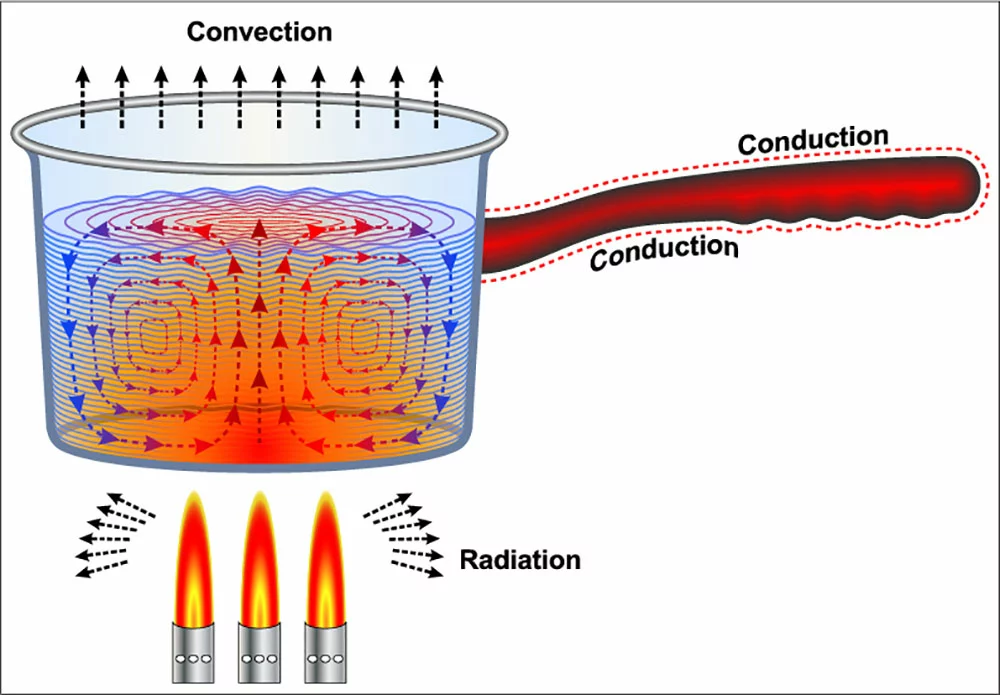
Heat transfer mechanisms
Strategies to Control Heat Flow
You can use several strategies to control the heat entering the home, including roof overhangs, awnings, and blinds. These devices effectively block energy from direct sunlight, reducing heat gain in a hot climate.
In addition to these external controls, you can use many ventilation and insulating methods to regulate heat loss within the home.
It is essential when keeping indoor spaces cool in the summer by blocking the sunlight from hitting any exposed absorbers.

Roof overhang
Ways to Make Your Home Passively Solar-Powered
Direct gain
It is a very common and simple form of passive solar heat gain. It occurs when the sun’s rays strike a dark surface, such as a wall or floor, and are absorbed as heat. The heat is then transferred to the air in the room, making it warmer.
Sun-tempering
This passive solar heating involves orienting a long wall containing most windows towards the true south. The wall will absorb solar energy and then transfer that heat to the interior of the home or building.
Indirect gain
This type uses thermal mass behind south windows. The thermal mass will absorb solar energy during the day and then slowly release it at night to heat the interior of a home or building.
It may also utilize a Trombe wall, a heavy masonry wall with an air gap between it and the south-facing windows. This air gap acts as a solar collector, heating the air inside, then venting it into other rooms for convection heating.
Isolated gain
This type of solar energy system uses a greenhouse-like structure to collect energy from the sun. Fans are then used to distribute the heated air, which can help to avoid overheating in the summer or provide warmth in cold climates.
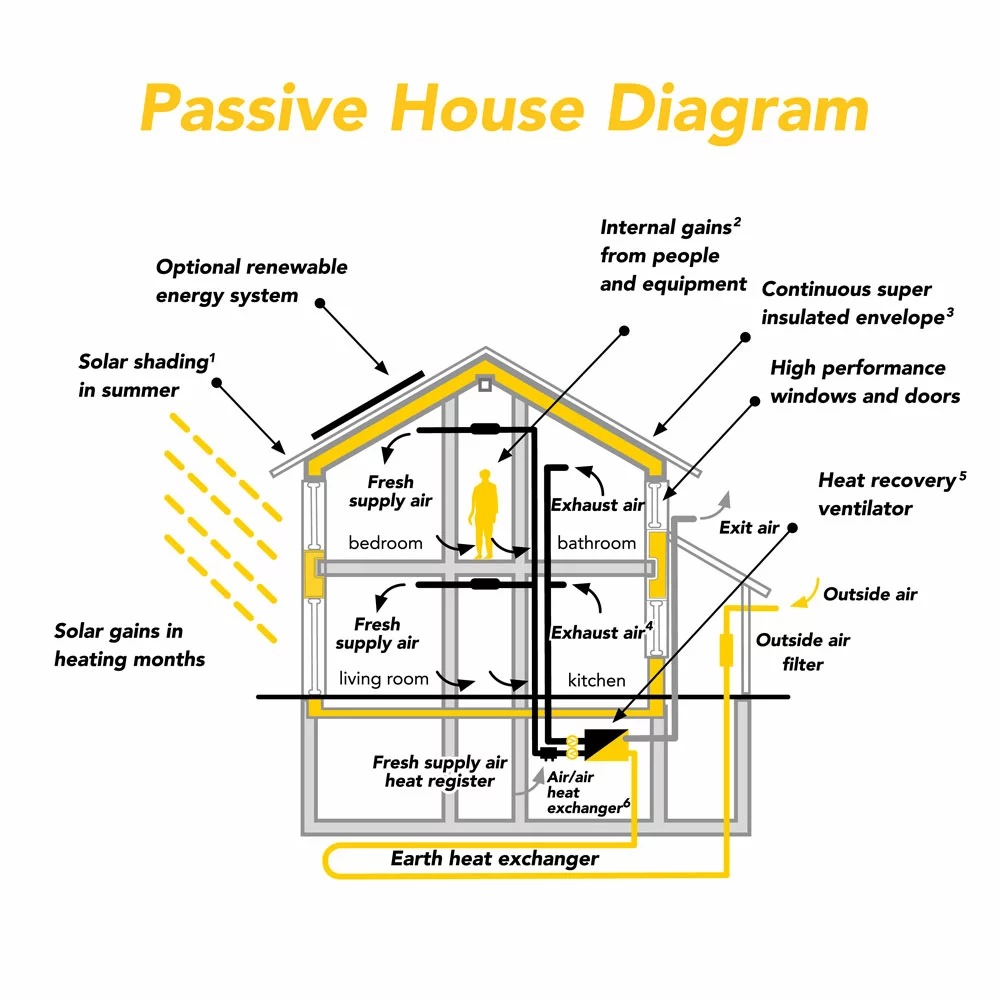
Passive House Diagram
Methods of Passive Solar Cooling
Shading
This method considers the sun’s natural movement all year round. In passive solar homes, you can use overhangs to prevent the sunlight from shining through a south-facing window in hot climates. These overhangs will also allow the light to shine at a lower angle during the winter.
Not to mention, the strategic placement of vegetation can help to keep a home cool in the late afternoon.
Ventilation
The placement of the building’s windows should be perpendicular to prevailing winds. There should be corresponding windows on the opposite side of the building too. It will allow for cross-ventilation and airflow, which is essential.
Convection
Convection occurs when hot air rises while cold air sinks. This movement transfers heat between objects and can also help create mini-currents within a building that carry heat away from hot areas and into cooler ones. You can achieve this by placing intake vents or using fans to encourage airflow throughout a room or building as needed.
Can Passive Solar Design Work with Solar Panels
These two technologies work together well. Passive solar techniques help keep your home cool on sunny days and reduce energy usage. This way, you can save money on your electric bill. Meanwhile, the photovoltaic panels turn the sun’s energy into electricity that you can use for all your needs – eliminating your reliance on fossil fuels and reducing your environmental footprint.
You can turn your home into a solar-powered one by using solar panels and incorporating passive solar techniques.
Active vs. Passive Solar Energy: Which Is More Efficient?
Active solar energy harnesses sunlight’s power through solar panels or other devices that convert sunlight into usable energy. Meanwhile, passive solar energy utilizes the properties of sunlight to naturally warm a home or building, minimizing the need for costly heating systems.
Which one is more efficient ultimately depends on your specific needs and priorities. For example, tinting your windows with a shading film may cost less. Still, it will offer only modest savings on your monthly utility bills.
On the other hand, installing solar panels can be expensive, but they can deliver significant savings over time. Ultimately, choosing between these two options will depend on your ROI goals and whether you are more interested in minimizing upfront costs or realizing long-term savings.

Solar panels on the roof of a house
Summary
Solar power is a great way to reduce energy costs and reliance on fossil fuels. In this article, we’ve explored two types of solar energy – passive and active. Passive solar energy uses natural methods, like shading and ventilation, whereas active solar energy uses technology, like solar panels.
Both options have their benefits, depending on your specific needs and priorities. Solar energy can lead to long-term savings and a smaller environmental footprint regardless of your option.
